[TOC]
SpringBoot 介绍
什么是 SpringBoot ?
SpringBoot 提供了一种快速使用 Spring 的方式,基于约定优于配置的思想,可以让开发人员不必在配置与逻辑业务之间进行思维的切换,全身心的投入到逻辑业务的代码编写中,从而大大提高了开发的效率,一定程度上缩短了项目周期。
2014 年 4 月,Spring Boot 1.0.0 发布,并作为 Spring 的顶级项目之一。

Spring 缺点
1)配置繁琐
- 虽然 Spring 的组件代码是轻量级的,但它的配置却是重量级的。一开始,Spring 用 XML 配置,而且是很多 XML 配置。Spring 2.5 引入了基于注解的组件扫描,这消除了大量针对应用程序自身组件的显式 XML 配置。Spring 3.0 引入了基于 Java 的配置,这是一种类型安全的可重构配置方式,可以代替 XML。
- 所有这些配置都代表了开发时的损耗。因为在思考 Spring 特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切换,所以编写配置挤占了编写应用程序逻辑的时间。
- 和所有框架一样,Spring 实用,但它要求的回报也不少。
2)依赖繁琐
- 项目的依赖管理也是一件耗时耗力的事情。在环境搭建时,需要分析要导入哪些库的坐标,而且还需要分析导入与之有依赖关系的其他库的坐标,一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题就会严重阻碍项目的开发进度。
SpringBoot 功能
1)自动配置
- SpringBoot 的自动配置是一个运行时(更准确地说,是应用程序启动时)的过程,考虑了众多因素,才决定 Spring 配置应该用哪个,不该用哪个。该过程是 SpringBoot 自动完成的。
2)起步依赖(依赖传递)
- 起步依赖本质上是一个 Maven 项目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。
- 简单的说,起步依赖就是将具备某种功能的坐标打包到一起,并提供一些默认的功能。
3)辅助功能
- 提供了一些大型项目中常见的非功能性特性,如嵌入式服务器、安全、指标,健康检测、外部配置等。
总结:
Spring Boot 并不是对 Spring 功能上的增强,而是提供了一种快速使用 Spring 的方式
。
SpringBoot 快速入门
需求:
- 搭建 SpringBoot 工程,定义 HelloController.hello() 方法,返回“Hello SpringBoot!”。
步骤:
- 创建 Maven 项目;
- 导入 SpringBoot 起步依赖:
<!--springboot工程需要继承的父工程--><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version></parent><dependencies><!--web开发的起步依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
- 定义 Controller:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class HelloController {@RequestMapping("/hello")public String sayHello() {return "Hello SpringBoot!";}}
- 编写引导类:
- controller 类必须是 Application 的所在包的类或者子包的类。
- 官网:程序只加载 Application.java 所在包及其子包下的内容。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringbootQuickDemoApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootQuickDemoApplication.class, args);}}
- 执行 main 方法,启动测试:


小结:
-
SpringBoot 在创建项目时,使用 jar 的打包方式。
-
SpringBoot 的引导类,是项目入口,运行 main 方法就可以启动项目。
-
使用 SpringBoot 和 Spring 构建的项目,业务代码编写方式完全一样。
IDEA 快速构建 SpringBoot 工程:


SpringBoot 起步依赖-原理概述
<!--springboot工程需要继承的父工程--><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version></parent><dependencies><!--web开发的起步依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
-
在 spring-boot-starter-parent 中定义了各种技术的版本信息,组合了一套最优搭配的技术版本。
-
在各种 starter 中,定义了完成该功能需要的坐标合集,其中大部分版本信息来自于父工程。
-
我们的工程继承 parent,引入 starter 后,通过依赖传递,就可以简单方便获得需要的 jar 包,并且不会存在版本冲突等问题。
SpringBoot 配置文件
配置文件类型
SpringBoot 是基于约定的,所以很多配置都有默认值,但如果想使用自己的配置替换默认配置的话,就可以使用 application.properties 或者 application.yml(application.yaml)进行配置。
# propertiesserver.port=8080# ymlserver:port: 8080
小结:
-
SpringBoot 提供了两种配置文件类型:properteis 和 yml/yaml
-
默认配置文件名称:application.properties(application 名称固定)
-
在同一级目录下优先级为:properties > yml > yaml
YAML 介绍
有关 YAML 的介绍与用法,可参考:《Java YAML 序列化》
读取配置内容
- 方式一:@Value
- 方式二:Environment
- 方式三:@ConfigurationProperties
代码示例:
- application.yml 配置文件内容:
name: outer_nameperson:name: xiaomingage: 18address:- shenzhen- shanghai- beijing# 配置tomcat启动端口server:port: 8082
- @ConfigurationProperties(对象注入):
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")public class Person {private String name;private int age;private String[] address;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String[] getAddress() {return address;}public void setAddress(String[] address) {this.address = address;}}
- Controller:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class HelloController {// 方式一:@Value 注入@Value("${name}")private String name;@Value("${person.name}")private String personName;@Value("${person.address[0]}")private String personFirstAddress;// 方式二:Environment 对象@Autowiredprivate Environment env;// 方式三:@ConfigurationProperties 对象注入@Autowiredprivate Person person;@RequestMapping("/hello")public String sayHello() {System.out.println(personName); // xiaomingSystem.out.println(personFirstAddress); // shenzhenSystem.out.println(env.getProperty("person.name")); // xiaomingSystem.out.println(env.getProperty("person.address[0]")); // shenzhenString[] address = person.getAddress();for (String add: address) {System.out.println(add);}/*shenzhenshanghaibeijing*/return "Get successfully!";}}
注意:以下提示不影响运行,在加了以下依赖后边不再有此提示,且在编写配置文件时会有友好提示。

<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency>

profile
我们在开发 SpringBoot 应用时,通常同一套程序会被安装到不同环境,比如:开发、测试、生产等。其中数据库地址、服务器端口等等配置都不同,如果每次打包时,都要修改配置文件的话,会非常麻烦。为此,profile 功能就是来进行动态配置切换的。
profile 的 2 种配置方式:
- 多 profile 文件方式:提供多个配置文件,每个代表一种环境
- application-dev.properties/yml (代表开发环境)
- application-test.properties/yml (代表测试环境)
- application-pro.properties/yml (代表生产环境)
- yml 多文档方式:
- 在 yml 中使用“—”(必须三个横杆)分隔不同配置
profile 的 3 种激活方式:
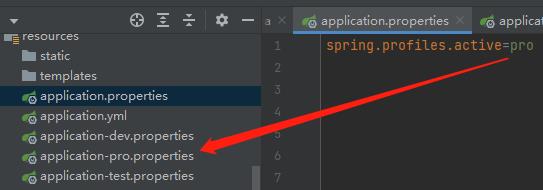
- 配置文件:在配置文件中配置 spring.profiles.active=dev
- 虚拟机参数:在 VM options 指定 -Dspring.profiles.active=dev
- 命令行参数:java –jar xxx.jar –spring.profiles.active=dev
代码示例:
-
多 profile 文件方式:
-
application.yml 多文档方式配置&激活:
# 配置开发环境server:port: 8081spring:profiles: dev---# 配置测试环境server:port: 8082spring:profiles: test---# 配置生产环境server:port: 8083spring:profiles: pro---# 使用配置文件激活profilespring:profiles:active: pro
内部配置文件加载顺序
Springboot 程序启动时,会从以下位置加载配置文件:
- 当前项目下的 /config 目录下(不会打进 jar 包)
- 当前项目的根目录(不会打进 jar 包)
- classpath 的 /config 目录下(classpath 即 resources 编译后的目录)
- classpath 的根目录
注意:
- 以上的优先级从高到低,相同的配置项,高优会覆盖低优。
- 若不同的配置项,则会互补而不会覆盖。
外部配置加载顺序
通过官网查看外部属性加载顺序:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/boot-features-external-config.html
SpringBoot 整合其他框架
整合 Junit
实现步骤:
- 搭建 SpringBoot 工程
- 引入 starter-test 起步依赖( IDEA 构建 SpringBoot 时自带)
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency>
- 编写测试类
- 添加测试相关注解
- Junit4@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
- @SpringBootTest(classes=main方法的启动类.class)
- Junit5
- @SpringBootTest(classes=main方法的启动类.class)
- 编写测试方法进行测试
整合 Redis
实现步骤:
- 搭建 SpringBoot 工程
- 引入 Redis 起步依赖(可使用 IDEA 快捷搭建与引入)

<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency>
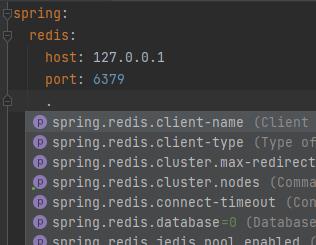
- 配置 Redis 相关属性(可选)
- 注入 RedisTemplate 模板
- 编写测试方法进行测试
代码示例:
- 测试类:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;@SpringBootTestclass DemoApplicationTest {@Autowiredprivate RedisTemplate redisTemplate; // 无配置情况下,默认连接本地redis(localhost:6379)@Testvoid testSet() {// 存入数据redisTemplate.boundValueOps("name").set("xiaoming");}@Testvoid testGet() {// 取数据Object name = redisTemplate.boundValueOps("name").get();System.out.println(name);}}
- (application)添加 Redis 配置:
整合 Mybatis
实现步骤:
- 搭建 SpringBoot 工程
- 引入 Mybatis 起步依赖、添加 Mysql 驱动

<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>2.2.1</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId></dependency>
- 编写 DataSource 和 MyBatis 相关配置
- 定义表和实体类
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`;CREATE TABLE `t_user` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`username` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,`password` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;insert into `t_user`(`id`,`username`,`password`) values (1,\'zhangsan\',\'123\'),(2,\'lisi\',\'234\');
- 编写 dao 和 mapper 文件/纯注解开发
- 测试
注解版
- application.yml:
spring:datasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql:///world?serverTimeZone=UTC # 默认连接本地3306username: rootpassword: admin
- UserMapper:
package com.example.mybatis_demo.mapper;import com.example.mybatis_demo.domain.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import java.util.List;@Mapper@Repositorypublic interface UserMapper {@Select("select * from t_user")public List<User> findAll();}
- 测试类:
import com.example.mybatis_demo.mapper.UserMapper;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTestclass MybatisDemoApplicationTests {@AutowiredUserMapper userMapper;@Testvoid testFindAll() {userMapper.findAll().forEach(user -> System.out.println(user));}}
配置版
- UserXmlMapper:
package com.example.mybatis_demo.mapper;import com.example.mybatis_demo.domain.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import java.util.List;@Mapper@Repositorypublic interface UserXmlMapper {public List<User> findAll();}
- application.yml:
# datasourcespring:datasource:url: jdbc:mysql:///springboot?serverTimezone=UTCusername: rootpassword: rootdriver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver# mybatismybatis:mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml # mapper映射文件路径type-aliases-package: com.itheima.springbootmybatis.domain# config-location: # 指定mybatis的核心配置文件
- UserMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.example.mybatis_demo.mapper.UserXmlMapper"><select id="findAll" resultType="user">select * from t_user</select></mapper>
- 测试类:
import com.example.mybatis_demo.mapper.UserXmlMapper;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTestclass MybatisDemoApplicationTests {@AutowiredUserXmlMapper userMapper;@Testvoid testFindAll() {userMapper.findAll().forEach(user -> System.out.println(user));}}
 爱站程序员基地
爱站程序员基地





