join()方法:将数组中所有元素通过指定分隔符连接成一个字符串
举例:
myArr.join(\'-\') // 用\'-\'符号拼接
concat()方法:将两个数组或多个数组合并成一个数组
举例:
myArr.concat(arr1, arr2, ..., arrN)
注意:该方法不会改变现有的数组,所以可以和空数组合并实现复制旧数组,在操作新数组数据时不污染旧数组数据
sort() 方法:用于对数组的元素进行排序
如果调用该方法时没有使用参数,将按字母顺序对数组中的元素进行排序,说得更精确点,是按照字符编码的顺序进行排序。要实现这一点,首先应把数组的元素都转换成字符串(如有必要),以便进行比较
举例:
myArr.sort() // 按字母排序myArr.sort(function(a, b) {return a - b}) // 按数字升序,降序为b - a// 箭头函数写法myArr.sort((a, b) => a - b)
reverse() 方法:用于颠倒数组中元素的顺序
举例:
myArr.reverse()
push() / unshift()方法:向数组的末尾 / 开头添加一个或多个元素,并返回新的长度
举例:
myArr.push(item1, item2, ..., itemN)myArr.unshift(item1, item2, ..., itemN)
shift()方法:删除数组的第一个元素,并返回第一个元素的值
举例:
myArr.shift()
pop()方法:删除数组的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
举例:
myArr.pop() // 删除数组最后一个元素myArr.pop(1) // 删除数组中索引为1的元素
splice()方法:向/从数组中添加/删除项目,然后返回被删除的项目
myArr.splice(index, count, item1, item2, ..., itemN)// index 必需。整数,规定添加/删除项目的位置,使用负数可从数组结尾处规定位置// count 必需。要删除的项目数量。如果设置为 0,则不会删除项目// item1, item2, ..., itemN 可选。向数组添加的新项目
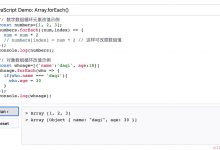
forEach()方法:方法用于调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数(相当于for循环)
举例:
myArr.forEach(function (item, index, arr) {if (index === 3) {item = 123}}) // 循环数组,将索引为3的元素值更改为123// 箭头函数写法myArr.forEach((v, i, arr) => if (i === 3) { v = 123 })
注意:以下方法均不会对空数组进行检测,不会改变原始数组
indexOf()方法:查找数组是否存在某个元素,返回下标,没有则返回-1
举例:
myArr.indexOf(item)
注意:indexOf() 方法对大小写敏感!
slice()方法:可提取字符串的某个部分,并以新的字符串返回被提取的部分(浅拷贝数组的元素)
举例:
const newArr = myArr.slice(0, 1)// 截取数组myArr索引从0到1的部分元素// 参数:// begin(可选): 索引数值,接受负值,从该索引处开始提取原数组中的元素,默认值为0。// end(可选):索引数值(不包括),接受负值,在该索引处前结束提取原数组元素,默认值为数组末尾(包括最后一个元素)
every()方法:用于检测数组中的元素是否满足指定条件(函数提供)(如某个值是否都为true)
如果有一个元素不满足,则整个表达式返回 false,且停止检测;如果所有元素都满足条件,则返回 true
举例:
const state = myArr.every(function (item, index, arr) {return item > 10}) // 检测数组myArr的所有元素是否都大于10,返回一个布尔值state// 箭头函数写法const state = myArr.every((v, i, arr) => v > 10)
some()方法:用于检测数组中的元素是否满足指定条件(函数提供)(如某个值是否都为true)
如果有一个元素满足,则整个表达式返回 true ,且停止检测;如果没有满足条件的元素,则返回false
举例:
const state = myArr.some(function (item, index, arr) {return item > 10}) // 检测数组myArr中是否存在元素大于10,返回一个布尔值state// 箭头函数写法const state = myArr.some((v, i, arr) => v > 10)
includes()方法:用于判断数组是否包含指定的值,如果找到匹配的值则返回 true,否则返回 false
注意:includes() 方法区分大小写
参数:
searchvalue:必需,要查找的值
start:可选,设置从那个位置开始查找,默认为 0
举例:
const state = myArr.includes(3) // 检测数组myArr中是否存在元素3,返回一个布尔值stateconst state = myArr.includes(3, 3) // 从索引3开始检测数组myArr中是否存在元素3,返回一个布尔值state
filter()方法:创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素
举例:
const newArr = myArr.filter(function (item, index, arr) {return item > 10}) // 检测数组myArr中所有元素都大于10的元素,返回一个新数组newArr// 箭头函数写法const newArr = myArr.filter((v, i, arr) => v > 10)
map()方法:返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值
map()方法按照原始数组元素顺序依次处理元素
举例:
const newArr = myArr.map(function (item, index, arr) {return item * 10}) // 数组myArr中所有元素都乘于10,返回一个新数组newArr// 箭头函数写法const newArr = myArr.map((v, i, arr) => v * 10)
举例(用于数组嵌套对象的类型):
const newArr = myArr.map(function (item, index, arr) {return {id: item.id,newItem: \'123\'}}) // 处理数组myArr中指定的对象元素里面的元素或新元素,返回一个新数组newArr// 箭头函数写法const newArr = myArr.map((v, i, arr) => {return {id: v.id,newItem: \'123\'}})
find() / findIndex()方法:返回通过测试(函数内判断)的数组的第一个元素的 值 / 索引。如果没有符合条件的元素返回 undefined / -1
举例:
const val = myArr.find(function (item, index, arr) {return item > 10}) // 返回数组myArr中第一个大于10的元素的值val,没有则返回undefinedconst val = myArr.findIndex(function (item, index, arr) {return item > 10}) // 返回数组myArr中第一个大于10的元素索引,没有则返回-1
reduce()方法:返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值
这个方法接收两个参数:要执行的函数,传递给函数的初始值
要执行的函数(total, currentValue, currentValue, arr):
total:必选,初始值, 或者计算结束后的返回值
currentValue:必选,当前元素;
currentValue:可选,当前元素索引;
arr:可选,当前元素所属的数组对象
举例1:
const myArr = [1, 2, 3]const sum = myArr.reduce(function(pre, cur, index, arr) {console.log(pre, cur)return pre + cur})console.log(sum)// 输出值分别为// 1, 2// 3, 3// 6
举例2(设置初始迭代值):
const myArr = [1, 2, 3]const sum = myArr.reduce(function(pre, cur, index, arr) {console.log(pre, cur)return prev + cur}, 2)console.log(sum)// 输出值分别为// 2, 1// 3, 2// 5, 3// 8
应用:
1.求和、求乘积
const myArr = [1, 2, 3, 4]const result1 = myArr.reduce(function(pre, cur) {return pre + cur})const result2 = myArr.reduce(function(pre, cur) {return pre * cur})console.log(result1) // 6console.log(result2) // 24
2.计算数组中每个元素出现的次数
const myArr = [\'liang\',\'qi\',\'qi\',\'liang\',\'ge\',\'liang\']const arrResult = myArr.reduce((pre,cur) =>{if(cur in pre){pre[cur]++}else{pre[cur] = 1}return pre},{})console.log(arrResult) // 结果:{liang: 3, qi: 2, ge: 1}
3.对对象的属性求和
const myArr = [{name: \'liangqi\',weigth: 55},{name: \'mingming\',weigth: 66},{name: \'lele\',weigth: 77}]const result = myArr.reduce((a,b) =>{a = a + b.weigthreturn a},0)console.log(result) // 结果:198
Array.of()方法:用于将一组值转化为新数组
举例:
Array.of() // []Array.of(undefined) // [undefined]Array.of(1) // [1]Array.of(1, 2) // [1, 2]
flat()方法:数组拍平方法也叫数组扁平化、数组拉平、数组降维,用于将嵌套的数组变成一维数组,返回一个新数组
举例:
const myArr = [1, [2, 3, [4, 5, [12, 3, \"zs\"], 7, [8, 9, [10, 11, [1, 2, [3, 4]]]]]]]console.log(myArr.flat(Infinity)) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 12, 3, \"zs\", 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 1, 2, 3, 4]
总结
到此这篇关于JS新手入门数组处理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JS数组处理内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- JS数组(Array)处理函数整理
- 在javascript将NodeList作为Array数组处理的方法
- js对ajax返回数组的处理介绍
- 用Javascript数组处理多个字符串的连接问题
- 在JavaScript中处理数组之reverse()方法的使用
- 在Javascript中处理数组之toSource()方法的使用
- JavaScript对象数组的排序处理方法
- js 处理数组重复元素示例代码
 爱站程序员基地
爱站程序员基地