定位(positio)
简介
- 定位是一种更加高级的布局手段,通过定位可以将元素摆放到页面的任意位置
- 使用position属性来设置定位static 默认值,元素是静止的没有开启定位
- relative 开启元素的相对定位
- absolute 开启元素的绝对定位
- fixed 开启元素的固定定位
- sticky 开启元素的粘滞定位
偏移量:当元素开启了定位以后,可以通过偏移量来设置元素的位置
bottom:定位元素和定位位置下边的距离
left:定位元素和定位位置的左侧距离
right:定位元素和定位位置的右侧距离
相对定位
- 当元素的position属性值设置为relative时则开启了元素的相对定位
- 特点元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化
- 相对定位是参照于元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的
- 相对定位会提升元素的层级
- 相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
- 相对定位不会改变元素的性质块还是块,行内还是行内
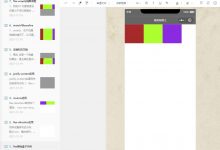
### 定位(positio)#### 简介- 定位是一种更加高级的布局手段,通过定位可以将元素摆放到页面的任意位置- 使用position属性来设置定位- static 默认值,元素是静止的没有开启定位- relative 开启元素的相对定位- absolute 开启元素的绝对定位- fixed 开启元素的固定定位- sticky 开启元素的粘滞定位- 偏移量:当元素开启了定位以后,可以通过偏移量来设置元素的位置- top:定位元素和定位位置上边的距离- bottom:定位元素和定位位置下边的距离- left:定位元素和定位位置的左侧距离- right:定位元素和定位位置的右侧距离#### 相对定位- 当元素的position属性值设置为relative时则开启了元素的相对定位- 特点- 元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化- 相对定位是参照于元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的- 相对定位会提升元素的层级- 相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流- 相对定位不会改变元素的性质块还是块,行内还是行内```css<!DOCTYPE html><html lang=\"en\"><head><meta charset=\"UTF-8\"><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0\"><meta http-equiv=\"X-UA-Compatible\" content=\"ie=edge\"><title>Document</title><style>body{font-size: 60px;}.box1{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #bfa;}.box2{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: orange;position: relative;left: 100px;top: -200px;}.box3{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;}</style></head><body><div class=\"box1\">1</div><div class=\"box2\">2</div><div class=\"box3\">3</div></body></html>
绝对定位
- 当元素的position属性值设置为absolute时,则开启了元素的绝对定位
- 特点:开启绝对定位后,如果不设置偏移量元素的位置不会发生变化
- 开启绝对定位后,元素会从文档流中脱离
- 绝对定位会改变元素的性质,行内变成块,块的宽高被内容撑开
- 绝对定位会使元素提升一个层级
- 绝对定位元素是相对于其包含块进行定位的
包含块
绝对定位的包含块:包含块就是离它最近的开启了定位的祖先元素,如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位则根元素就是它的包含块
html(根元素、初始包含块)
布局
left + margin-left + border-left + padding-left + width + padding-right + border-right + margin-right + right = 包含块的内容区的宽度
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang=\"en\"><head><meta charset=\"UTF-8\"><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0\"><meta http-equiv=\"X-UA-Compatible\" content=\"ie=edge\"><title>Document</title><style>body{font-size: 60px;}.box1{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #bfa;}.box2{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: orange;position: absolute;/* left: 0;top: 0; */bottom: 0;right: 0;}.box3{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;}.box4{width: 400px;height: 400px;background-color: tomato;position: relative;}.box5{width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: aliceblue;/* position: relative; */}</style></head><body><div class=\"box1\">1</div><div class=\"box4\">4<div class=\"box5\">5<div class=\"box2\">2</div></div></div><div class=\"box3\">3</div></body></html>
固定定位
- 将元素的position属性设置为fixed则开启了元素的固定定位
- 固定定位也是一种绝对定位,所以固定定位的大部分特点都和绝对定位一样
- 唯一不同的是固定定位永远参照于浏览器的视口进行定位,固定定位的元素不会随网页的滚动条滚动
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang=\"en\"><head><meta charset=\"UTF-8\"><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0\"><meta http-equiv=\"X-UA-Compatible\" content=\"ie=edge\"><title>Document</title><style>body{font-size: 60px;height: 2000px;}.box1{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #bfa;}.box2{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: orange;position: fixed;left: 0;top: 0;}.box3{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;}.box4{width: 400px;height: 400px;background-color: tomato;}.box5{width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: aliceblue;}</style></head><body><div class=\"box1\">1</div><div class=\"box4\">4<div class=\"box5\">5<div class=\"box2\">2</div></div></div><div class=\"box3\">3</div></body></html>
粘滞定位
- 当元素的position属性设置为sticky时则开启了元素的粘滞定位
- 粘滞定位和相对定位的特点基本一致,不同的是粘滞定位可以在元素到达某个位置时将其固定
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang=\"en\"><head><meta charset=\"UTF-8\"><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0\"><meta http-equiv=\"X-UA-Compatible\" content=\"ie=edge\"><title>导航条</title><link rel=\"stylesheet\" href=\"./css/reset.css\"><style>body{height: 3000px;}/* 设置nav的大小 */.nav{/* 设置宽度和高度 */width: 1210px;height: 48px;/* 设置背景颜色 */background-color: #E8E7E3;margin:100px auto;position: sticky;top: 10px;}/* 设置nav中li */.nav li{/* 设置li向左浮动,已使菜单横向排列 */float: left;/* 设置li的高度 *//* height: 48px; *//* 将文字在父元素中垂直居中 */line-height: 48px;}/* 设置a的样式 */.nav a{/* 将a转换为块元素 */display: block;/* 去除下划线 */text-decoration: none;/* 设置字体颜色 */color: #777777;/* 修改字体大小 */font-size: 18px;padding: 0 39px;}.nav li:last-child a{padding: 0 42px 0 41px;}/* 设置鼠标移入的效果 */.nav a:hover{background-color: #3F3F3F;color: #E8E7E3;}</style></head><body><!-- 创建导航条的结构 --><ul class=\"nav\"><li><a href=\"#\">HTML/CSS</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">Browser Side</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">Server Side</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">Programming</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">XML</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">Web Building</a></li><li><a href=\"#\">Reference</a></li></ul></body></html>
元素的层级
- 对于开启了定位元素,可以通过z-index属性来指定元素的层级
- z-index需要一个整数作为参数,值越大元素的层级越高,元素的层级越高越优先显示
- 如果元素的层级一样,则优先显示靠下的元素,祖先的元素的层级再高也不会盖住后代元素
 爱站程序员基地
爱站程序员基地