Contribution
proposed an interpretable deep model for fine-grained visual recognition:
- 做细粒度分类,但同时output the segmentation of object parts and the identification of their contributions towards classification,增加了模型的可解释性
- 为了确认object parts,使用a simple prior (prior knowledge)。利用assumption:给定一张图,某个part出现的概率符合Beta distribution(beta distribution具体没懂,之后再了解)。
Methods
-
region-based part discovery and attribution
输入图片。输出类别,assignment map(区域分割),attention map(标出重要区域)。分三步:
- compare input feature X with part dictionary D, 得到soft part assignment map Q.
- 根据Q 和D,从X中pool出region features Z。再根据Z 进一步计算attention a。
- 用a reweight Z,算出最终结果。

-
prior-based regularisation
文章用了一个assumption:

例如: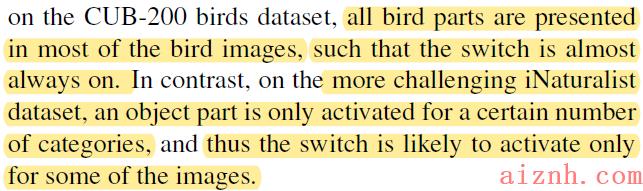
在loss里,除了CELoss以外,还有一个regularisation term,目的是通过缩减学习出的part probability 和prior knowledge的U-shape probability的1D Wasserstein distance来align他们. 文章用了一些数学trick来计算两者的distance,1D Wasserstein distance是什么也没太仔细看。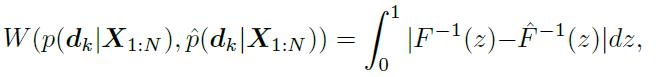
Results
和其他工作的可视化对比:

不只对比了分类结果,还量化的对比的interpretability(通过计算localisation error):

 爱站程序员基地
爱站程序员基地

![[翻译] Backpressure explained — the resisted flow of data through software-爱站程序员基地](https://aiznh.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/29-220x150.jpeg)