1.方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bbox(item, column=None) | 返回指定item的框选范围,或者单元格的框选范围 |
| column( cid, option=None, **kw) | 设置或者查询某一列的属性 |
| delete(*items) | 删除指定行或者节点(含子节点) |
| vdetach(*items) | 与delete类似,不过不是真正删除,而是隐藏了相关内容。可以用move方法重新显示v |
| exists(item) | 判断指定的item是否存在 |
| focus(item=None) | 获得选定item的iid,或者选中指定item。 |
| get_children(item=None) | 返回指定item的子节点 |
| heading(column, option=None, **kw) | 设置或者查询表头行的配置参数 |
| identify(component, x, y) | 返回在坐标(x,y)处的部件信息。部件包括:region(heading,cell等), item, column, row, 和 element。 |
| identify_element(x, y) | 返回在(x,y)处的元素。 |
| identify_region(x, y) | 返回坐标(x,y)处的Tree view组成部分 |
| identify_row(y) | 给定y坐标,返回指定item索引 |
| index(item) | 返回数字化的item索引,从0开始 |
| set_children(item, *newchildren) | 设置item的新子节点为newchildren,现有的子节点会被移除。一般用于树形结构中。 |
| insert(parent, index, iid=None, **kw) | 插入一个新的item |
| item(item, option=None, **kw) | 返回item节点的相关信息 |
| move(item, parent, index) | move()方法有两种作用: (1)将detach的item重新显示(reattach) (2)移动item指定的节点到parent的子节点中,位置由index指定 |
| next(item) | 返回item的下一个节点 |
| parent(item) | 返回item的父节点 |
| prev(item) | 返回item的前一个节点 |
| see(item) | 保证item指定的节点在Treeview控件中可见 |
| selection(items=None) | 返回当前选定的节点的iid |
| selection_set(*items) | 选中items指定的节点 |
| selection_remove(*items) | 从当前选择中移除items指定的节点 |
| selection_add(*items) | 将items指定的节点添加到当前的选择中 |
| selection_toggle(*items) | 选中的节点变为不选中,未选中的节点变为选中 |
| set(item, column=None, value=None) | 设置或者获得节点信息 |
| tag_bind( tagname, sequence=None, callback=None) | 给tagname指定的tag绑定事件以及回调函数 |
| tag_configure( tagname, option=None, **kw) | 配置或者获得tag的有关信息 |
| tag_has(tagname, item=None) | 判断tag是否存在或者是tag与那些节点关联 |
1.1 bbox(item, column=None)
获取指定item的框选范围。如果指定的item可见,返回值是一个四元组(x,y,w,h)。(x,y)是矩形框选的左上角坐标,(w,h)是矩形的宽度与高度。有这个四元组设定的矩形正好可以框选指定的item。如果column不为空,返回的是指定单元格的框选范围。
坐标值是以Treeview控件为基准的,而不是以窗口或者屏幕。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=7,padding=(10,5,20,30))for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def select(*args):print(tv.bbox(tv.selection()))print(tv.bbox(tv.selection(),column=\'c\'))tv.bind(\'<<TreeviewSelect>>\',select)root.mainloop()
结果:
(11, 50, 280, 20)
(151, 50, 70, 20)
说明:输出的结果有2个,一个是选中行的框选范围,一个是选中行的第三个单元格的框选范围。
1.2 column( cid, option=None, **kw)
查询或者修改指定列的配置。cid可以是整数,也可以列的别名。如果不输入option,则返回目前的配置选项字典。
Treeview列的选项有:
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| anchor | 对齐模式。取值有n,e,s,w,ne,nw,se,sw和center。 |
| id | 列的名称或者标识 |
| minwidth | 列的最小宽度,调整列宽的时候,不会小于这个数值。默认值是20 |
| stretch | 是否随着窗口大小的调整而拉伸Treeview。默认值是True |
| width | 定义列宽。默认值是200 |
查询代码:
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=7,padding=(10,5,20,30))for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])print(tv.column(3))root.mainloop()
结果:
{\’width\’: 70, \’minwidth\’: 20, \’stretch\’: 1, \’anchor\’: \’e\’, \’id\’: \’e\’}
设置代码:
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def column():tv.column(2,width=50)ttk.Button(root,text=\'Column\',command=column).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:

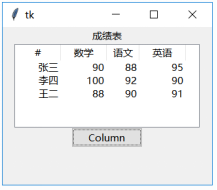
说明:点击\’Column\’按钮后,语文成绩那一列的宽度由70变为50。
1.3 delete(items)
删除指定的item。子节点也会被一起删除,但是第一层节点不会被删除。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def delete():tv.delete(tv.selection())ttk.Button(root,text=\'Delete\',command=delete).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:


1.4 detach(items)
detach的方法与delete类似,不过detach不是真正的删除了指定的item,而是隐藏了内容,可以使用move的方法重新将隐藏的数据再显示出来。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])detach=Noneindex=Nonedef detach():global detachglobal indexdetach=tv.selection()index=tv.index(detach)tv.detach(detach)def attach():global detachglobal indexif detach:tv.move(detach,\'\',index)ttk.Button(root,text=\'Detach\',command=detach).pack()ttk.Button(root,text=\'Attach\',command=attach).pack()root.mainloop()
说明:先选中一行,然后点击\’Detach\’按钮,此时会将选中的行隐藏。但是相关的id和index会依旧被记录。再点击\’Attach\’按钮,使用move()方法就会重新显示隐藏的数据。
1.5 exists(item)
判断指定的item是否存在。需要注意的是,使用detach()方法隐藏的item会被认为是存在的,因为相应的id等信息是依然被系统记录没有清空的。返回值为True,如果指定的item不存在,否则返回False。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])print(tv.exists(\'I002\'))root.mainloop()
结果:
结果为True
1.6 focus(item=None)
focus()方法有三种情况:
(1)有item被选中同时参数为None
返回当前被选中的item的标识iid
(2)无item被选中同时参数为None
返回空字符串\’\’
(3)输入item参数
指定的item会获得focus。
注意:获得focus不表示被选中。
#有item被选中同时参数为None,返回iidimport tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def focus():print(tv.focus())ttk.Button(root,text=\'Focus\',command=focus).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:

结果为:I003

#无item被选中同时参数为None#item参数不为空import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def focus():tv.focus(\'I002\')print(tv.focus())ttk.Button(root,text=\'Focus\',command=focus).pack()root.mainloop()
注:使用focus()方法,并不会让获得focus的item被高亮显示。如果要高亮显示,请使用selection_set()方法。
1.7 get_children(item=None)
返回指定item的子节点。如果该item没有子节点返回None。如果没有指定节点,默认返回root节点的子节点。
1.8 heading(column, option=None, **kw)
设置或者查询表头行的配置参数。如果是表格形式的,column是列的位置(就是第几列,从0计数)或者列的别名。如果是树形结构的(比如文件目录),column的值为\’#0\’。
如果没有option参数,返回的是当前的配置数据。
heading的选项有:
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| anchor | 对齐模式。取值有n,e,s,w,ne,nw,se,sw和center。 |
| command | 与指定列相关的回调函数 |
| image | 在表头显示图片 |
| text | 在表头显示文本 |
| state | 当前列的状态 |
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def heading():print(tv.heading(column=1))ttk.Button(root,text=\'Heading\',command=heading).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:
{\’text\’: \’数学\’, \’image\’: \’\’, \’anchor\’: \’center\’, \’command\’: \’\’, \’state\’: \’\’}
1.9 identify(component, x, y)
返回在坐标(x,y)处的部件信息。部件包括:region(heading,cell等), item, column, row, 和 element。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def identify():print(tv.identify(\'region\',120,30))ttk.Button(root,text=\'Identify\',command=identify).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:
cell
1.10 identify_column(x)
给定x坐标,返回所属的列号。返回值的格式是\’#n\’。n是从1开始计数的列号。注意返回的是实际的显示列号,而不是逻辑定义的列号。如果使用了displaycolumns就可以实际显示的列号与columns定义的列号是不一致的情况。具体的用法与identify类似,可以参考。
1.11 identify_element(x, y)
返回在(x,y)处的元素。使用方法是: tv.identify_element(140,25)
1.12 identify_region(x, y)
返回坐标(x,y)处的Tree view组成部分。Treeview 的组成部分有:
| 组成部分 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| nothing | 不在Treeview控件内 |
| heading | 位于表头的位置 |
| separator | 在分隔线上 |
| tree | 位于图标列(树形列表表示展开/折叠的图标) |
| cell | 位于单元格内 |
使用方法是:
tv.identify_region(140,25)
1.13 identify_row(y)
给定y坐标,返回指定item索引(如‘I002\’)。如果没有内容,返回空字符串。
使用方法:
tv.index(‘I002\')
1.14 index(item)
返回数字化的item索引,计数从0开始。使用方法:
tv.index(‘I002\')
1.15 set_children(item, newchildren)
设置item的新子节点为newchildren,现有的子节点会被移除。一般用于树形结构中。
tv.set_children(\'I003\',\'I00E\')
说明:将I00E作为新的I003的子节点。
1.16 insert(parent, index, iid=None, **kw)
插入一个新的item。
(1)parent
对于表格类型的Treeview,parent一般为空。对于树形类型的Treeview,parent为父节点。
(2)index
指明在何处插入新的item。可以是\’end\’,也可以是数字。比如,如果要让新插入的item成为第一个子节点或者在第一行,index就设为0。如果是第二个子节点或者第二行,就是设置index=1。如果在最末端插入item,就设置index=\’end\’
(3)iid
如果没有赋值,就使用系统自动生成的id。如果输入了id,必须保证与现有的id不重复。否则系统会自动生成id。
(4)**kw
设置插入item的属性。支持的属性有:
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| image | 显示图像 |
| open | 针对树形结构,确认插入的item是打开还是折叠状态。True打开,False为折叠。 |
| tags | 为新插入的item设置tag标签 |
| text | 显示文字 |
| values | 在表格结构中,要显示的数值。这些数值是按照逻辑结构赋值的,也就是按照columns设定的列次序来赋值。如果输入的个数少于columns指定列数,则插入空白字符串 |
在前面章节的例子中已经使用了insert,可以参考。
1.17 item(item, option=None, **kw)
item()方法有3种功能:
(1)只有item参数
返回item有关数据字典。数据字典的键值(key)包括:
text,image,open,tags以及values。values就是item参数指定的节点的内容。
tv.item(\'I002\')
结果:
{\’text\’: \’\’, \’image\’: \’\’, \’values\’: [\’李四\’, 100, 92, 90], \’open\’: 0, \’tags\’: \’\’}
(2)输入item和option参数
返回item指定节点中由option指定的选项值。比如:
tv.item(\'I002\',option=\'values\')
就是返回节点的内容。见前一节有关返回数据字典的键值。
(3)item和kw
使用kw中的键值对(就是选项值)修改item指定的节点的相关选项。最常用的是使用values来修改节点的内容。
比如:
tv.item(\'I002\',values=(\'李峰\',\'90\',\'88\',\'66\'))
结果:


可以看到第二行的数据被修改了。
1.18 move(item, parent, index)
move()方法有两种作用:
(1)将detach的item重新显示(reattach)
(2)移动item指定的节点到parent的子节点中,位置由index指定
需要注意的是,不能把父节点移动到子节点下面。因为这是无法实现的。还有就是index的值如果是0或者负数,则表示item的位置在parent的第一个子节点。如果index的值大于或者等于子节点的总数,则表示把item放置在子节点的最后一个。
1.19 next(item)
(1)如果item不是当前父节点的最后一个子节点,则返回下一个子节点
(2)如果item已经是最后一个子节点,返回空字符串
(3)如果是表格类型的Treeview,则返回下一item对象。或者返回空字符串如果item已经是最后一个item对象。
1.20 parent(item)
树形结构的Treeview,该方法返回父节点的ID;如果是表格类型的Treeview,则返回空字符串。
1.21 prev(item)
与next()类似,不过是返回前一个item的ID。
1.22 see(item)
保证item指定的节点在Treeview控件中可见。针对有比较多节点的情况下,此方法可以让希望显示的节点快速显示在窗口中而不需要用滚动条的去滚动。
1.23 selection(items=None)
返回当前选定的节点的iid。
1.24 selection_set(items)
选中item指定的节点。items可以是单个节点的ID,或者多个节点ID的元组。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i])def selection():tv.selection_set(\'I001\',\'I002\')ttk.Button(root,text=\'Selection\',command=selection).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:

1.25 selection_remove(items)
与selection_set()相反,selection_remove()是把items指定的节点从选择中移除。
1.26 selection_add(items)
将items指定所有节点加入到选中的集合中。那么selection_add()与selection_set()的区别是什么?selection_set相当于重置选择的节点,不管以前是如何选择的,执行selection_set后,只有selection_set中输入的items节点会被选中。而selection_add()对当前的选选择没有影响,只是把items指定的节点添加到选择的集合中。
1.27 selection_toggle(items)
该方法的作用相当于数字电路中的非门,就是已经选中的节点变为为选中,没有选中的节点变为选中。
1.28 set(item, column=None, value=None)
(1)只有item
返回指定节点(行)的数据字典。字典的键值是columns属性定义的列的别名,而对应的数值就是节点(行)的内容。此种用法相当于获取指定节点的行内容与列别名信息。
(2)只有item和column
返回由item和column指定的单元格的内容。column的取值是别名。
tv.set(\'I002\',column=\'all\')
(3)item,column和value
如果三个参数都有值,那么会修改由item和column指定的单元格的内容。
tv.set(\'I002\',column=\'all\',value=\'abc\')
1.29 tag_bind( tagname, sequence=None, callback=None)
将tagname指定的tag与sequence指定事件绑定,回调函数由callback设定。需要注意的是,一个tag可能与多个节点相关。也就是说,可能会有多个item与事件绑定。
import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkroot = tk.Tk()root.geometry(\'320x240\')tk.Label(root,text=\'成绩表\').pack()area=(\'#\',\'数学\',\'语文\',\'英语\')ac=(\'all\',\'m\',\'c\',\'e\')data=[(\'张三\',\'90\',\'88\',\'95\'),(\'李四\',\'100\',\'92\', \'90\'),(\'王二\',\'88\',\'90\', \'91\')]tv=ttk.Treeview(root,columns=ac,show=\'headings\',height=5)for i in range(4):tv.column(ac[i],width=70,anchor=\'e\')tv.heading(ac[i],text=area[i])tv.pack()for i in range(3):tv.insert(\'\',\'end\',values=data[i],tags=str(i))def tb(*args):print(*args)def bind():tv.tag_bind(\'1\',sequence=\'<Button-1>\',callback=tb)ttk.Button(root,text=\'Bind\',command=bind).pack()root.mainloop()
结果:
<ButtonPress event state=Mod1 num=1 x=131 y=61>
说明:给插入的数据每一行都设定一个tag,比如第一行的tag是\’0\’,等等。然后通过tag_bind()方法绑定鼠标左键事件。
1.30 tag_configure( tagname, option=None, **kw)
与item()方法有些类似,也是有三种功能:
(1)只有tagname
返回tagname指定tag的选项/属性数据字典。比如tv.tag_configure(‘2\’)的返回值为:
{‘text\’: ‘\’, ‘image\’: ‘\’, ‘anchor\’: ‘\’, ‘background\’: ‘\’, ‘foreground\’: ‘\’, ‘font\’: ‘\’}
(2)tagname和option
返回tagname指定的tag中option指定的属性值。比如option=\’anchor\’,则返回anchor属性值。
(3)tagname和kw
对tagname指定的tag,使用kw中的参数设置有关属性。属性值见(1)中的说明。
1.31 tag_has(tagname, item=None)
(1)只有tagname
返回所有与tagname指定的tag有关的子节点。
(2)tagname和item
如果item指定的子节点的有tagname指定的tag,则返回True,否则返回False。判断tag是否存在。
到此这篇关于Python tkinter 树形列表控件(Treeview)的使用方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python tkinter 树形列表内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- python3使用tkinter实现ui界面简单实例
- Python tkinter模块弹出窗口及传值回到主窗口操作详解
- Python升级提示Tkinter模块找不到的解决方法
- Python Tkinter简单布局实例教程
- Python 窗体(tkinter)下拉列表框(Combobox)实例
- 对Python 窗体(tkinter)树状数据(Treeview)详解
- Python tkinter label 更新方法
- python 实现在tkinter中动态显示label图片的方法
- Python tkinter的grid布局及Text动态显示方法
- Python中使用Tkinter模块创建GUI程序实例
 爱站程序员基地
爱站程序员基地

